rfid chip agriculture Using RFID to improve irrigation is revolutionary for improving soil quality, enhancing workflow and ensuring proper water distribution across the farm. RFID tags enable . With Mark Brunell still rusty, Jacksonville asked Fred Taylor to carry the load Sunday. He delivered with one of the best playoff games ever for a rookie back. Fish foil Flutie in fantastic finish .
0 · what is rfid used for
1 · rfid monitoring in agriculture
2 · rfid for agriculture
3 · plant health management rfid
Some 4G LTE devices use a NFC nano SIM card, which is the same size as a regular Nano SIM Card with an additional level of security that protects your .
Using RFID to improve irrigation is revolutionary for improving soil quality, enhancing workflow and ensuring proper water distribution across the farm. RFID tags enable . The development of RFID applications in precision agriculture makes possible to increase efficiencies, productivity and profitability while minimizing unintended impacts on wildlife and the environment, in many agricultural production systems. Using RFID to improve irrigation is revolutionary for improving soil quality, enhancing workflow and ensuring proper water distribution across the farm. RFID tags enable crops to be watered equally and on time. Farmers can also use the tech to read and analyze water quality and nutrient levels, allowing troubleshooting before it is distributed . There are many uses for RFID technology in agriculture. Bales of hay can be tagged, capturing the date harvested, the field where it was harvested, the temperature, weight, moisture level and the nutritional information to be captured and stored.
RFID chip company is playing a pivotal role in revolutionizing agriculture through precision farming applications. By leveraging RFID technology, farmers can enhance efficiency, optimize resource allocation, and minimize environmental impact.
Mandatory electronic identification, or radio-frequency identification (RFID) has been discussed for well over a decade at the USDA-APHIS and appears to be likely in the near future to become USDA policy unless we can succeed at explaining the burden on smaller independent producers. In precision agriculture, RFID technology plays a key role in tracking crop growth and yield. Farmers can attach RFID tags to crops or use integrated RFID sensors in the soil to monitor environmental conditions like soil moisture and temperature.
smart card stages
But the RFID chips send out a signal, which is captured by a reader that uploads information into a database. They are in common use in industries including logistics and amusement parks. The U.S. Department of Agriculture supports the idea of using RFID tags to track cattle that cross state lines.
This paper first introduces RFID sensing technology, then surveys its applications to the four areas of agriculture: plant growing environment, soil conditions, plant growth, and the quality of. The main goals of employing RFID technology in agriculture are to improve agro-food productions and yields and reduce labor and time costs. Smart farming that put emphases on precision and automation also benefit greatly from RFID applications. The aim of this paper is to review the numerous applications that utilize RFID in agriculture and food industry and to classify them in appropriate categories. The analysis of their characteristics and contributions could be useful for perceiving new applications or relevant research opportunities.
The development of RFID applications in precision agriculture makes possible to increase efficiencies, productivity and profitability while minimizing unintended impacts on wildlife and the environment, in many agricultural production systems.
Using RFID to improve irrigation is revolutionary for improving soil quality, enhancing workflow and ensuring proper water distribution across the farm. RFID tags enable crops to be watered equally and on time. Farmers can also use the tech to read and analyze water quality and nutrient levels, allowing troubleshooting before it is distributed . There are many uses for RFID technology in agriculture. Bales of hay can be tagged, capturing the date harvested, the field where it was harvested, the temperature, weight, moisture level and the nutritional information to be captured and stored.RFID chip company is playing a pivotal role in revolutionizing agriculture through precision farming applications. By leveraging RFID technology, farmers can enhance efficiency, optimize resource allocation, and minimize environmental impact. Mandatory electronic identification, or radio-frequency identification (RFID) has been discussed for well over a decade at the USDA-APHIS and appears to be likely in the near future to become USDA policy unless we can succeed at explaining the burden on smaller independent producers.
In precision agriculture, RFID technology plays a key role in tracking crop growth and yield. Farmers can attach RFID tags to crops or use integrated RFID sensors in the soil to monitor environmental conditions like soil moisture and temperature. But the RFID chips send out a signal, which is captured by a reader that uploads information into a database. They are in common use in industries including logistics and amusement parks. The U.S. Department of Agriculture supports the idea of using RFID tags to track cattle that cross state lines.
This paper first introduces RFID sensing technology, then surveys its applications to the four areas of agriculture: plant growing environment, soil conditions, plant growth, and the quality of. The main goals of employing RFID technology in agriculture are to improve agro-food productions and yields and reduce labor and time costs. Smart farming that put emphases on precision and automation also benefit greatly from RFID applications.
smart card sydney
smart card top up ucc
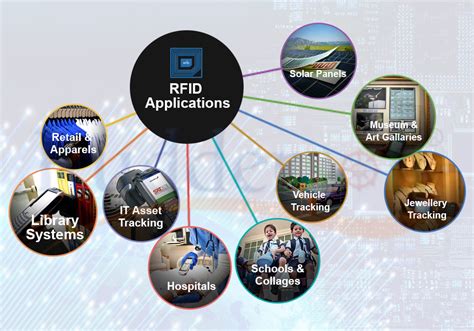
what is rfid used for
1989 NFC Wild Card Game: Los Angeles Rams LA 21 @ Philadelphia Eagles PHI 7: 12/31/89: 1989 AFC Wild Card Game: Pittsburgh Steelers PIT 26 @ Houston Oilers HOU 23: 01/06/90: .
rfid chip agriculture|plant health management rfid